Human Penis Anatomy: Insights & Images | Expert Guide
Is the human penis simply a functional organ, or is it a source of constant curiosity and, at times, insecurity? The truth is, the penis is a complex and fascinating part of the male anatomy, deserving of accurate information and a healthy perspective.
From the root, anchoring the organ to the body, to the sensitive glans, covered by the foreskin in uncircumcised individuals, the penis is a carefully crafted structure. It serves as a conduit for both urine and semen, essential functions for survival and reproduction. Understanding its intricate workings, from the mechanics of an erection to the process of ejaculation, is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of male health and sexuality. Images often illustrate the male external reproductive organs in their erect condition, displaying the penis and scrotum, offering a visual guide to the anatomy. The images below often show a variety of normal and abnormal anatomy of the male penis, including the difference between the circumcised and uncircumcised penis, phimosis, penile skin bridges, peyronies disease, genital warts, and tight frenulum of the penis, also known as frenulum breve of the penis.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Basic Function | External sex organ and part of the male urogenital tract, serving as a conduit for urine and delivering semen. |
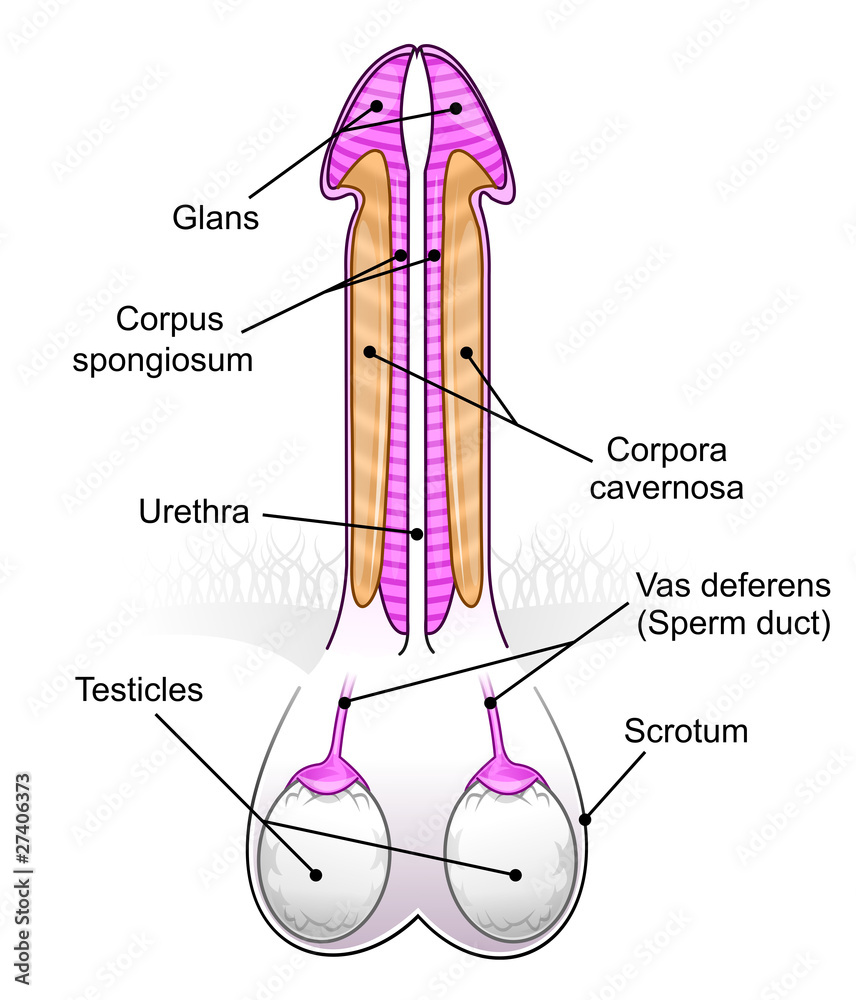
| Anatomy | Consists of the root (base), shaft (body), glans (head), and foreskin (prepuce) in uncircumcised males. |
| Root | Attaches to the pubic bone and surrounding tissues. |
| Shaft | The long, cylindrical portion extending from the root to the glans. |
| Glans | The head of the penis, covered by the foreskin in uncircumcised males. |
| Urethra | The external opening of the urethra, used for urination and semen delivery. |
| Size and Shape | Varies; normal erect penises are usually 5.1 to 5.5 inches long. The natural shape of the penis varies. |
| Common Conditions | Includes phimosis, penile skin bridges, Peyronies disease, genital warts, and tight frenulum (frenulum breve). |
| Erection | A physiological process enabling sexual function. |
| Ejaculation | The expulsion of semen. |
| Reproductive System Role | Functions as part of the male reproductive system, along with the testes and surrounding structures. |
| Myth Busting | Dispelling myths about penis size, shape, and appearance. |
| Medical Information | Schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional for any concerns. |
| Visual Information | A frenulum of human penis.jpg 6,000 4,000; |
| Educational Resources | The images below show a variety of normal and abnormal anatomy of the male penis, including the difference between the circumcised and uncircumcised penis, phimosis, penile skin bridges, peyronies disease, genital warts, and tight frenulum of the penis, also known as frenulum breve of the penis. |
| External Resource | Mayo Clinic - Penis Anatomy |
The images that often accompany discussions on this topic are varied and serve different purposes. Some provide a clear visual representation of normal anatomy, allowing individuals to familiarize themselves with the expected appearance of a healthy penis. These images are invaluable in dispelling misconceptions and promoting body positivity. It's a fact that a diverse range of shapes, sizes, and appearances exist within the realm of normal penis anatomy. These images can help individuals to feel confident.
Beyond the purely aesthetic, understanding the penis also means recognizing the potential for variations and conditions. The images below show a variety of normal and abnormal anatomy of the male penis, including the difference between the circumcised and uncircumcised penis, phimosis, penile skin bridges, peyronies disease, genital warts, and tight frenulum of the penis, also known as frenulum breve of the penis. Some males experience phimosis, a condition where the foreskin is too tight to retract. Others may encounter Peyronie's disease, which can cause curvature or deformity of the penis. Genital warts, a sexually transmitted infection, can also affect the penis. These conditions underscore the importance of regular self-examination and professional medical advice. It's worth noting that the penis, as an external organ, is also susceptible to injuries.
Furthermore, the penis is a dynamic organ, undergoing significant changes throughout the life cycle. It reaches its full size during puberty, a physical marker of the transition into adulthood. From an anatomical perspective, the penis is an external sex organ and, additionally, serves as the urinary duct.
The foreskin, a retractable fold of skin covering the glans in uncircumcised males, serves a protective function. The glans itself is a highly sensitive region, rich in nerve endings that contribute to sexual sensation. The shaft of the penis, composed of erectile tissue, is the structure responsible for achieving an erection. The penis is, therefore, a delicate interplay of structure and function. The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans.
The penis is not just a conduit for urination; it's also an instrument of sexual function. It plays a pivotal role in the mechanics of sexual reproduction. The penis contains the external opening of the urethra, which is used for urination and to deliver semen into the vagina of a female sexual partner. The process of sexual arousal leads to an erection. As sexual stimulation increases, blood flow to the penis intensifies, causing the erectile tissue to become engorged and the penis to become rigid and erect. The culmination of this process is ejaculation, the release of semen containing sperm, a fundamental step in the reproductive cycle.
The penis also holds a place within the broader context of male urogenital health. Issues related to the penis can sometimes be indicative of broader health problems. Therefore, regular check-ups, open communication with healthcare providers, and a proactive approach to health are all essential parts of maintaining a healthy penis.
In a culture saturated with often unrealistic representations of the male body, it's imperative to counter negative messages and promote a healthy body image. The penis comes in all shapes and sizes, and it is normal to have a penis of any shape, size, or appearance. The focus should be on function and healthy practices rather than a rigid adherence to societal standards. They help get rid of false ideas about male private parts.
While theres a wealth of information available online and in medical resources, the best approach is to develop a comprehensive understanding of this important organ. This includes being able to differentiate between normal and abnormal anatomical features, recognizing potential signs of health issues, and knowing when to seek professional medical advice. Science shows normal erect penises are usually 5.1 to 5.5 inches long. The penis is the male external excretory and sex organ.
From an anatomical perspective, the penis is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) that additionally serves as the urinary duct. In human anatomy, the penis (\/ \u02c8pi\u02d0n\u026as \/; From the latin p\u0113nis, initially tail [1]) is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urinate and ejaculate. The penis is part of the male urogenital tract, and it is also a sexual reproduction organ. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. These images teach us about the natural shape of the penis.
In conclusion, the penis is far more than just a physical structure; it's a symbol of masculinity, a critical element of the male urogenital system, and a focal point for both physical and psychological well-being. By fostering open conversations, prioritizing accurate information, and championing a positive self-image, we can transform how we perceive and interact with this vital organ. Media in category anatomy of the human penis the following 84 files are in this category, out of 84 total. Articles relating to the human penis, an external male sex organ (intromittent organ) that additionally serves as the urinary duct.The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans. Discover normal penis anatomy through informative pictures, understanding variations in size, shape, and appearance, including common conditions like phimosis and penile curvature, to promote healthy male genitalia and dispel myths about penis anatomy.